AI : 7 Concepts You Must Master to Stay Ahead in the Future
When the whole world is talking about AI—its implications, advantages, and disadvantages—it’s our responsibility to take a step forward in understanding it. If we’re not ready, the world will move on without us, and we won’t get another chance to jump on that wagon.
Now is the time to understand and use AI the right way—so we can upgrade our lives, be more productive, and work more efficiently. I’ve tried my best to explain AI and everything related to it in the simplest way possible. Let’s dive in.
What is AI?
AI is simply a technology that helps computers and other machines mimic what the human brain does.
Our brain has developed through learning, making decisions, solving problems, creating new things, and taking responsibility for those actions. Likewise, AI helps machines think, solve problems, and make decisions.
Read more about AI in everyday life here – AI in Everyday life , AI tackling climate change
A Quick History of AI
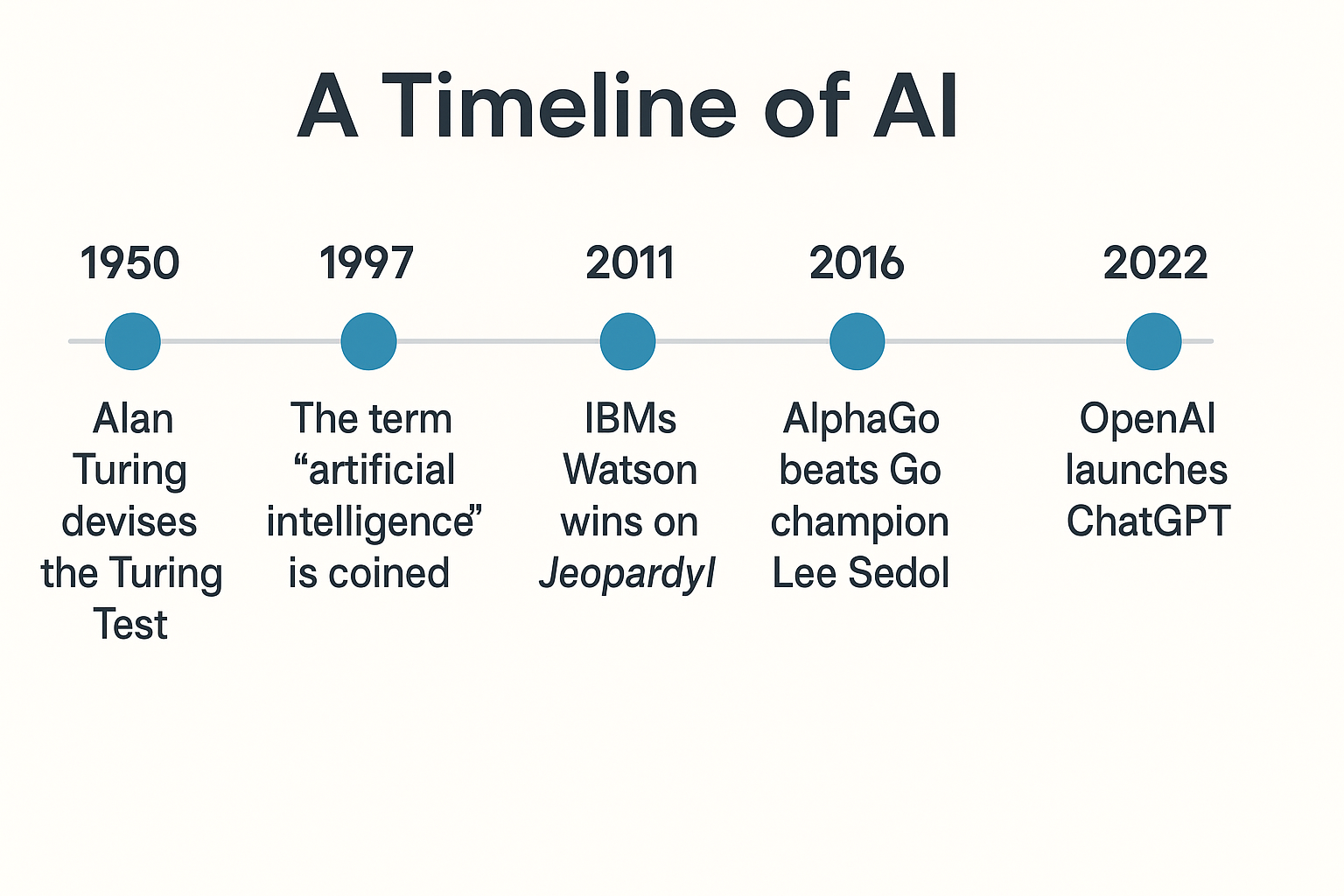
When we hear “AI,” we often think of OpenAI, Google Gemini, DeepSeek, or Grok. But these are just end products.
The story of AI began almost a century ago when Alan Turing famously asked: “Can machines think like humans?”
From that point on, AI evolved into the technology we now use daily. One of its earliest breakthroughs was Machine Learning.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI where we create models that can make predictions or decisions by studying and understanding the data we give them. This became possible through neural networks—a set of interconnected “neurons” (computing units) that pass information from one to the next.
Think of it like a group of people passing notes:
Each person reads the note, changes it slightly based on their understanding, and passes it on. Over time, the group learns to write the perfect note to answer a question.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is the next step in AI’s evolution. It uses multiple layers of neural networks to understand data more deeply. With more layers, machines can detect increasingly complex patterns.
Example:
- Machine Learning: You tell the computer the features—“Has fur,” “4 legs,” “Barks.”
- Deep Learning: You show it thousands of dog pictures, and it figures out those features on its own.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of deep learning model that can create new content—stories, songs, poems, reviews, even suggestions based on your text.
Popular examples include OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, Grok, and other AI tools you’ve probably heard about.
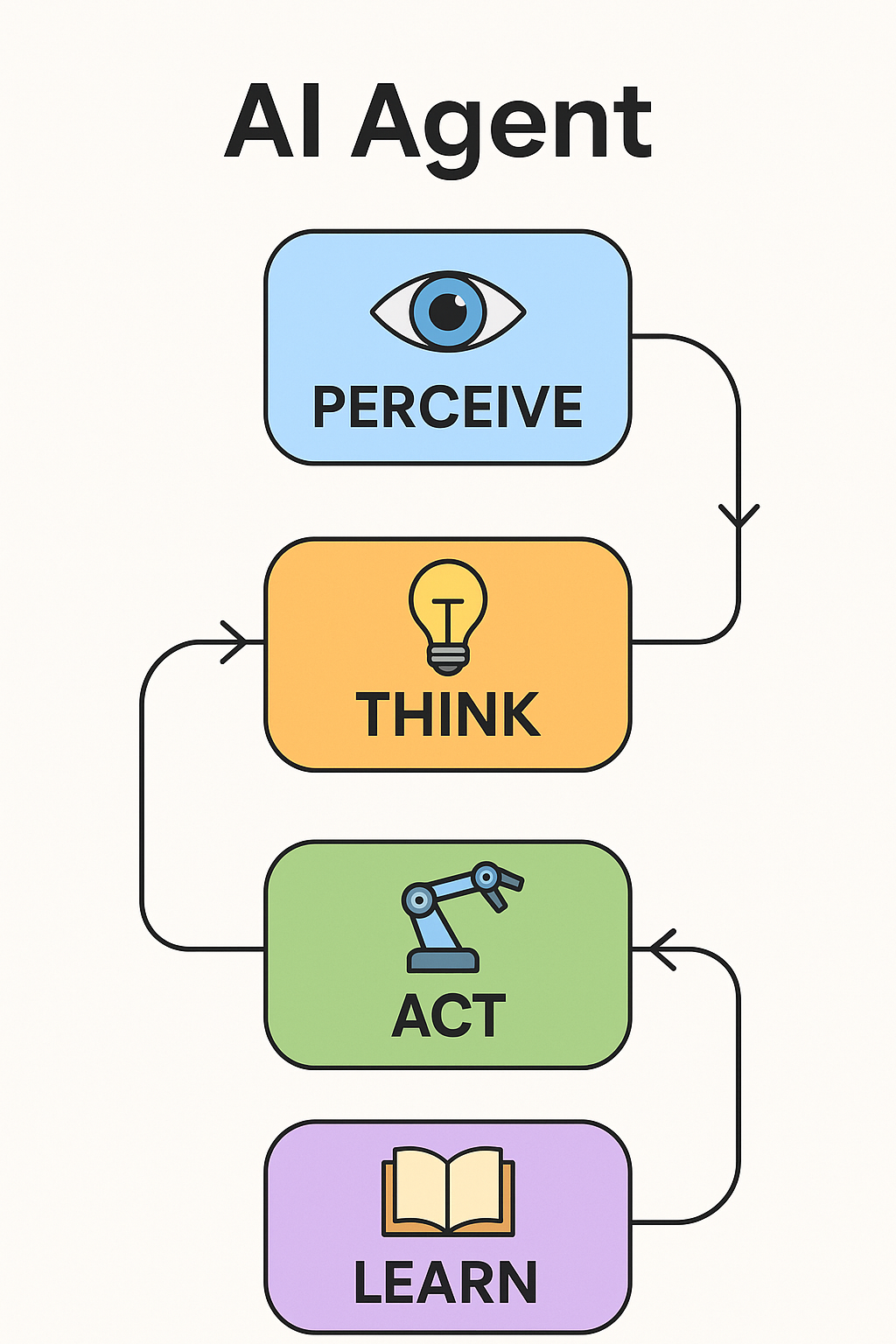
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an autonomous program that can complete tasks on your behalf—without your constant input—once you’ve set it up.
Example:
Imagine you have a little robot called Buddy whose job is to care for your puppy while you’re away.
You simply say: “Make sure my puppy is happy and safe until I’m back.”
Buddy will then:
🥎 Play fetch if the puppy is bored
🍖 Give food and water when the bowl is empty
🚪 Close the door if the puppy tries to run outside
🛌 Put the puppy to bed if it’s tired
It observes, decides, and acts all on its own—just like a real AI agent in the tech world.
Agentic AI is simply a group of AI agents working together to complete complex tasks.
Read more about AI agents here – AI Agents
Challenges with AI
- Accountability
Who’s responsible if AI gives bad advice or takes harmful action—AI itself or its creators? - Data Risk
AI collects the data you give it (and infers more from your conversations). Without complete data, it can’t work well—but “complete” might include sensitive personal info. Where do we draw the line? - Security
AI is still just a program, and no firewall is unbreakable. If hackers feed it corrupt data, its understanding of the world can be completely wrong. How can we ensure AI stays safe and trustworthy?
Final Thoughts
The world is evolving so quickly that it’s easy to miss what’s happening in between the big changes.
Self-aware, decision-making AI is still science fiction—but the AI we have now can still transform our lives if we learn to use it wisely.
Those who fail to adapt will be left behind. The world won’t slow down for you—so learn, adapt, evolve, and never stop.
If you want to learn more about AI and its developments check out this article by IBM



Pingback: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): 7 Essential Insights for Winning in the AI-First Search Era - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: Autonomous AI Agents: NEW WAY OF Decision-Making IN 2025 - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: AI and COGNITIVE Thinking: An IMPORTANT 2025 Guide to Staying Human - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: Stop the Fraud: How AI Protects Seniors from scams in 2025 - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: Autonomous Decision-Making AI: The Intelligent Systems of 2025 - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: AgentOps in 2025: A Practical Runbook to Monitor, Test & Govern Autonomous decision making AI Agents - ScienceThoughts
Pingback: Deepfake Dangers in 2025: How to Spot, Prevent & Stay Protected - ScienceThoughts