Stem Cell Research: 3 Breakthroughs, Benefits, and Future Prospects
A few years back, when we had to transplant an organ or if someone had an incurable disease, our options were very minimal and often far from ideal. But today, we are studying how to grow a healthy organ instead of taking it from someone else or finding ways to stop a cancer cell from developing instead of accepting our fate. We have come a long way in the field of medicine, and one of the many reasons for this development is stem cell research. Even though we are still far from fully realizing its potential, we no longer have to walk in the dark without knowing what lies on the other side. Knowing that solutions are within sight is better than giving up. In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into the world of stem cells and explore the remarkable developments in this field.
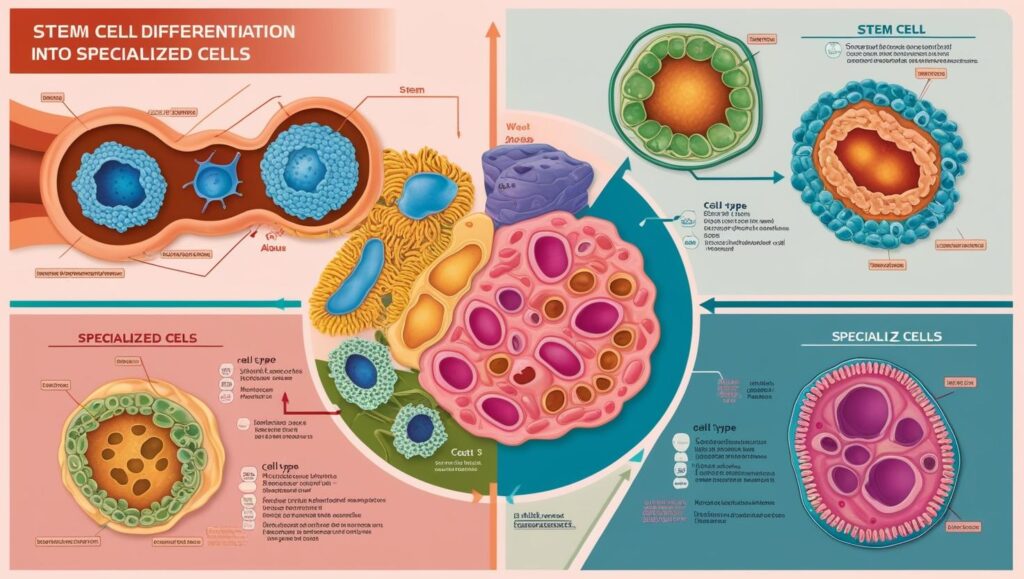
What is Stem Cell Research?
Stem cell research revolves around the study and application of stem cells—undifferentiated cells capable of transforming into specialized cell types. These cells play a crucial role in development, repair, and regeneration. There are three primary types of stem cells:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Derived from early-stage embryos, these cells are pluripotent, meaning they can develop into any cell type in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in tissues like bone marrow, skin, and fat, these cells are multipotent and more limited in their differentiation capacity compared to embryonic stem cells.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells, offering an ethical and versatile alternative.
Stem cell research seeks to harness the potential of these cells to treat diseases, understand developmental biology, and push the boundaries of medical science.
Recent Developments in Stem Cell Research
Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in the field of stem cell research:
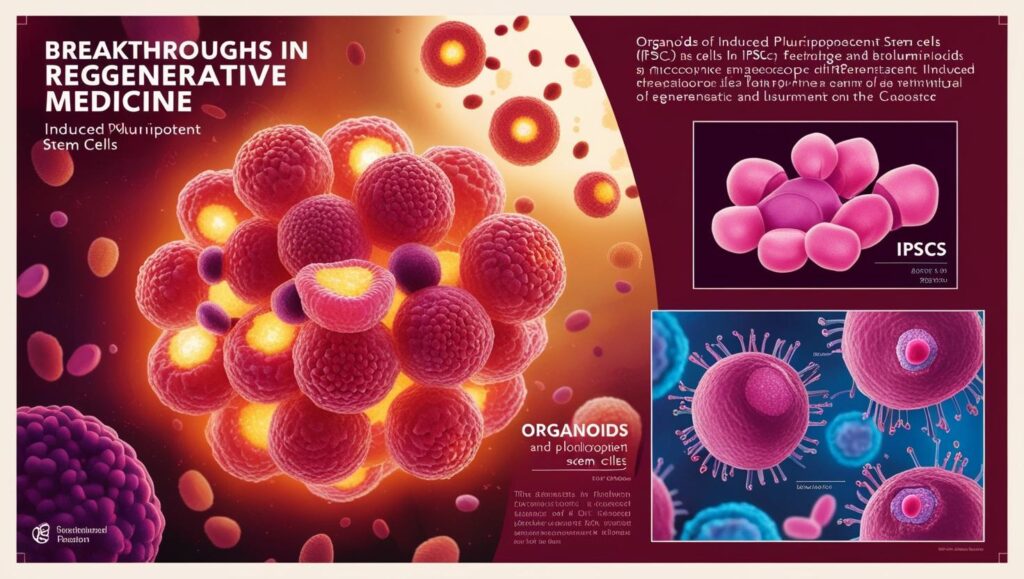
- Advancements in iPSC Technology: Researchers have improved methods for creating iPSCs, making them more efficient and safer for clinical applications. These cells are being explored for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
- Breakthroughs in Regenerative Medicine: Scientists have successfully grown organoids—miniature, simplified versions of organs—using stem cells. These organoids are revolutionizing drug testing and disease modeling for conditions like Alzheimer’s and cystic fibrosis.
- CRISPR and Gene Editing: Combining stem cell research with CRISPR technology has allowed precise genetic modifications, offering potential cures for genetic disorders such as sickle cell anemia and Huntington’s disease.
- Stem Cell Therapy for Vision Restoration: Clinical trials using stem cells to treat age-related macular degeneration and other vision disorders have shown promising results, offering hope for millions with impaired sight.
- Cancer Treatments: Research into cancer stem cells is opening new avenues for targeted therapies that aim to eradicate the root causes of tumor growth.
Benefits of Stem Cell Research
The potential applications of stem cell research are vast, promising to transform medicine and improve countless lives. Some key benefits include:
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cells can repair or replace damaged tissues, offering hope for conditions such as spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and diabetes.
- Personalized Medicine: Stem cells enable the creation of tailored treatments, minimizing side effects and maximizing efficacy.
- Drug Development and Testing: Stem cells provide a platform to test new drugs in a lab, reducing the need for animal testing and ensuring safety and effectiveness.
- Understanding Diseases: By studying stem cells, scientists gain insights into how diseases develop, paving the way for preventive strategies.
- Reducing Organ Transplant Shortages: Stem cell research could lead to the growth of replacement organs, addressing the critical shortage of donor organs.
Ethical Considerations and Future Prospects
While stem cell research offers immense potential, ethical debates, particularly around the use of embryonic stem cells, continue to shape the field. However, advancements in iPSCs and adult stem cells are mitigating these concerns.
The future of stem cell research looks incredibly promising, with ongoing studies exploring treatments for neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and genetic diseases. As science progresses, stem cell research is set to revolutionize healthcare, bringing us closer to a future where many currently incurable diseases become manageable or even curable.
Stem cell research exemplifies the power of innovation, holding the promise of a healthier, more sustainable future for humanity. By staying informed and supporting advancements in this field, we can contribute to a world where medical miracles become a reality.
Please read our latest blogs here


